- Photorefractive Keratectomy ( PRK )
- Laser keratomileusis ( LASIK )
- Phototherapeutic keratectomy ( PTK )
- Sclerostomy to treat glaucoma
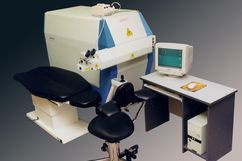
- UV ophthalmic laser system Medilex is designed for ophthalmology, i.e., to correct anomalies of eye refraction, such as myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.
- Medilex makes it possible to correct myopia by the methods of photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) or laser keratomileusis LASIK using microkeratom. At the corrections of anomalies of eye refraction, the radius of curvature of the cornea surface is changed.
- Medilex treats various eye cornea pathologies by the PTK method. With PTK, the irregular corneal surface is smoothed, and damaged opaque layers are removed.
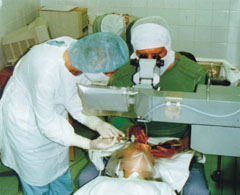
- Medilex allows effective treatment of eye diseases, such as glaucoma, with a shorter recovery time.
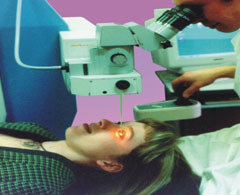
- Medilex operation is based on pulsed ablation of submicron layers of the cornea without any thermal damage. Shortwave UV laser emission is safe for internal eye tissues (lens and retina). Laser treatment provides high quality of the cornea surface and does not damage the initial transparency of the cornea.
- A computerized system controls the parameters of the system and the regime of operations.
- Medilex is characterized by low cost of the working gas mixture and is economical in work.
Technical Specifications
| Laser data | Equipment | |||
| Laser type | ArF or KrCl Excimer Laser | Surgical microscope | Carl Zeiss OPMI-1FC | |
| Wavelength | 193 nm or 223 nm | Optical delivery system | “Medilex” | |
| Max. pulse energy | 250 mJ | Soft Ware | ||
| Repetition rate | 10 pps | Computer | ||
| Pulse duration | Approx. 15 ns | Monitor | Digital Color TFT,15″ | |
| Ablation area | 0.5-7 mm | Microkeratom | for LASIK | |
| Fluence | 120-200 mJ/cm2 | Patient bed | Schwind | |
| Aiming Laser | Laser Diode 633 nm | Doctor’s chair | Schwind | |
| Focusing Laser | DPSS-module 532 nm |
| Device data | |
| Laser dimensions | 1718 х 1260 х 1416 mm |
| Basic device weight | Approx. 400 kg, total |
| Cooling | Air |
| Power reguirments | 220 V, single-phase, 50 Hz |
| Power consumption | 500 W |
| Gas supply | 2 internal 10 l ArF premix gas cylinder |
Additional Information
- V.V.Lantuch, A.M. Razhev et al. UV excimer lasers in eye microsurgery // Lasers in the Life Sciences, 1988, v.2, № 4, pp.271-284
- “Un Dispositivo de Correccion de Anomalias de Refreccion del Ojo”. Patente de Invencion, Espana, № solicitud 8902371, № publicacion 2014730. 16 July 1990. Priority: SU 11 July 1988, № 4457772.
- “Device for correcting ocular refraction anomalies”. United States Patent № 4.953.969. Published: Sep.4 1990. Priority: Jul.11 1988 USSR № 4457772.
- S.N. Bagayev, A.M. Razhev, A.A. Zhupikov. Excimer Laser Ophthalmic Devices for Eye Microsurgery // Laser Physics, 1998, v.8, №3, p.794-798.
- S.N. Bagayev, A.M. Razhev, A.A. Zhupikov. New 223 nm Excimer Surgical System for Photorefractive Keratectomy. // Proc.SPIE, 1998, v.3564, p.94-100.
- S.N. Bagayev, A.M. Razhev, A.A. Zhupikov, E.S. Kargapoltsev. Advantages of using the 223-nm compared with 193-nm radiation wavelength for ophthalmic applications”. Proc. SPIE, 2002, v.4900, p.1007-1013.
Contact Address
| Postal address: Prof. S.N. Bagayev, Institute of Laser Physics SB RAS, Ac.Lavrentyev’s prosp., 13/3, Novosibirsk, 630090 Russia |
Phone: +7(383) 333-24-89 Fax: +7(383) 333-20-67 E-Mail: bagayev@laser.nsc.ru |
